0 >>
contents
start

| TOC | Start here >> |
0 >> contents start |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
| Trends in Web Applications |
<< 1 >> contents start |
The Triumph of the Web |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Trends in Web Applications |
<< 2 >> contents start |
Many challenges facing application developers |
|---|---|
 |
|
Need for new design methodology
|
|
| Trends in Web Applications |
<< 3 >> contents start |
Proliferation of Servers, Languages, OS'es | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||||
|
||||||
| Trends in Web Applications |
<< 4 >> contents start |
Proliferation of Clients |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Trends in Web Applications |
<< 5 >> contents start |
Increasing Interaction and Customization |
|---|---|
 |
|
|
|
|
| Trends in Web Applications |
<< 6 >> contents start |
Open Source supports shared development | ||
|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||
|
|||
| Trends in the Web Infrastructure |
<< 7 >> contents start |
The Rise of XML |
|---|---|
 |
|
|
|
|
| Trends in the Web Infrastructure |
<< 8 >> contents start |
Challenges for Web Application Developers |
|---|---|
 |
|
|
|
|
| Challenges for Web Application Developers |
<< 9 >> contents start |
Which platform? | |
|---|---|---|
 |
||
|
platform = ( server, OS, language )
|
||
| Challenges for Web Application Developers |
<< 10 >> contents start |
How to Collaborate? Develop? Maintain? | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||||
|
Many people involved in the design, development, and maintenance
|
||||||
| Challenges for Web Application Developers |
<< 11 >> contents start |
Conventional Web development |
|---|---|
 |
|
 Application consists of documents, and some separate code |
|
| Challenges for Web Application Developers |
<< 12 >> contents start |
PIA-based Web Development |
|---|---|
 |
|
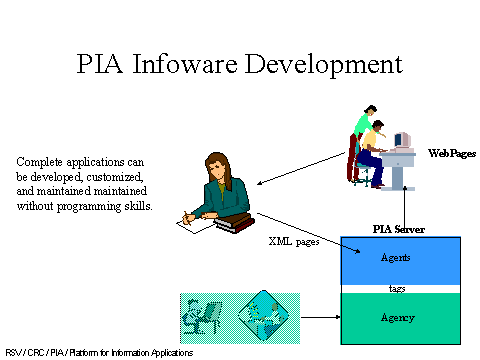 Application consists almost entirely of XML documents with a portable, standard processing engine. |
|
| The PIA Solution: an XML-based framework |
<< 13 >> contents start |
The PIA's Answers: cross-platform XML |
|---|---|
 |
|
|
|
|
| The PIA Solution: an XML-based framework |
<< 14 >> contents start |
PIA Features |
|---|---|
 |
|
|
|
|
| The PIA Solution: an XML-based framework |